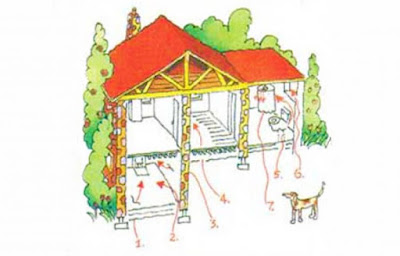
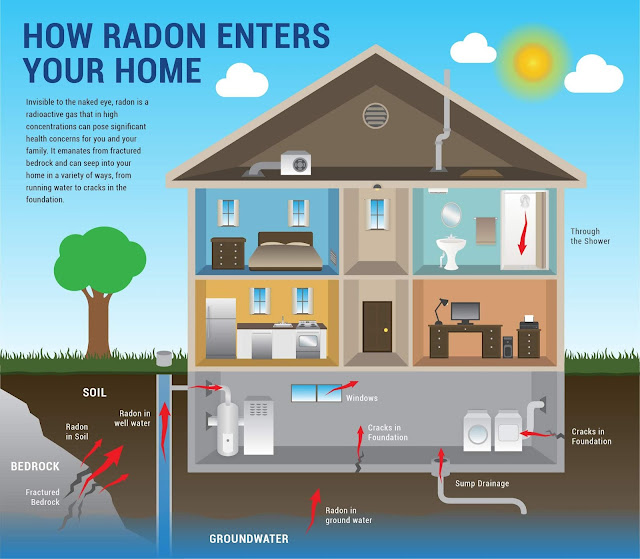
How Does Radon Enter a Home or Building?
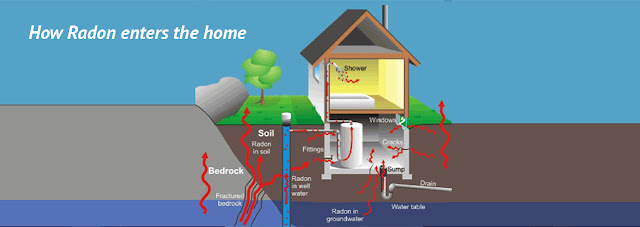
Radon forms naturally. Uranium in soil or rock breaks down to form radium, which then turns into radon gas. Once formed, radon enters a home through cracks in walls, basement floors, foundations and other openings. As radon decays, it releases radioactive byproducts that are inhaled and can cause lung cancer. Because radon comes from rock and soil, it can be found anywhere. Exposure to limited concentrations, like those found outdoors, is impossible to avoid. However, when radon gets trapped indoors, it may exist in dangerous concentrations. Less frequently, radon may enter buildings from water used in bathroom showers and faucets. Concerns have also been raised about the radon released indoors from building materials, such as granite countertops or tiles. However, these sources have rarely proven to be a problem by themselves. 2, 3 Concerns have also recently emerged about radon in natural gas extracted by hydraulic fracturing, or fracking. 4 Follow-up research has fo